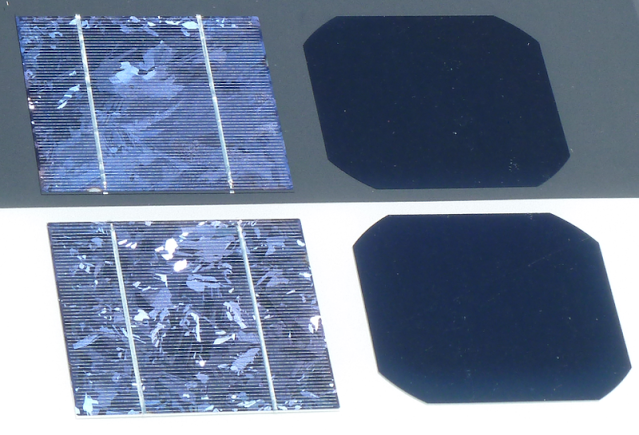
In single-crystal silicon, also known as monocrystalline silicon, the crystalline framework is homogeneous, which can be recognized by an even external colouring. The entire sample is one single, continuous and unbroken crystal as its structure contains no grain boundaries. Large single crystals are rare in nature and can also be difficult to produce in the laboratory (see also recrystallisation). In contrast, in an amorphous structure the order in atomic positions is limited to short range.
Polycrystalline and paracrystalline phases are composed of a number of smaller crystals or crystallites. Polycrystalline silicon (or semi-crystalline silicon, polysilicon, poly-Si, or simply "poly") is a material consisting of multiple small silicon crystals. Polycrystalline cells can be recognized by a visible grain, a "metal flake effect". Semiconductor grade (also solar grade) polycrystalline silicon is converted to single-crystal silicon – meaning that the randomly associated crystallites of silicon in polycrystalline silicon are converted to a large single crystal. Single-crystal silicon is used to manufacture most Si-based microelectronic devices. Polycrystalline silicon can be as much as 99.9999% pure. Ultra-pure poly is used in the semiconductor industry, starting from poly rods that are two to three meters in length. In microelectronic industry (semiconductor industry), poly is used both at the macroscale and microscale (component) level. Single crystals are grown using the Czochralski method, zone melting and Bridgman techniques.